4.00g/(mol) You can obtain the molar mass of any chemical element by using the periodic table: The molar mass is usually listed underneath the chemical symbol. The units associated with molar mass is grams per mole (g/(mol)). Helium gas is a non-toxic and non-combustible gas that is obtained from natural gas. Helium Gas was first detected in sun. It is available abundantly and is the second lightest gas seen. 4.00g / mol is the molar mass of helium. Dsp plugin for mac.
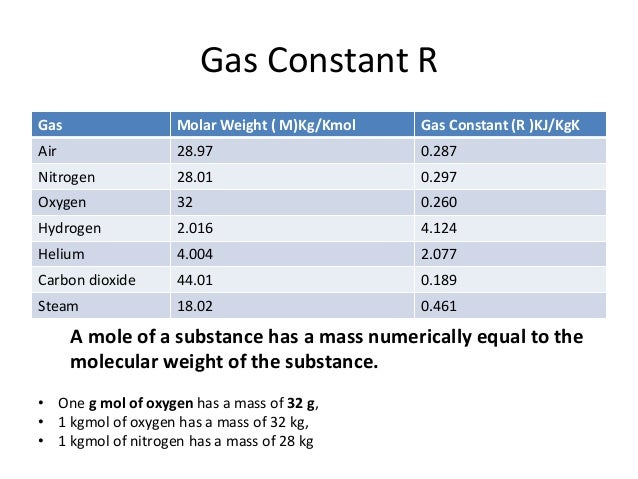
Specific heat at constant volume, specific heat at constant pressure, specific heat ratio and individual gas constant - R - common gases as argon, air, ether, nitrogen and many more .
The specific heat (= specific heat capacity) at constant pressure and constant volume processes, and the ratio of specific heats and individual gas constants - R - for some commonly used 'ideal gases', are in the table below (approximate values at 68oF (20oC) and 14.7 psia (1 atm)).

Helium-3 atom is the stable isotope of helium with relative atomic mass 3.016029. The least abundant (0.000137 atom percent) isotope of naturally occurring helium.It contains a helion.
For conversion of units, use the Specific heat online unit converter.
See also tabulated values of specific heat capacity of food and foodstuff, metals and semimetals, common liquids and fluids, common solids and other common substances as well as values of molar heat capacity of common organic substances and inorganic substances.
Molar Mass Table
For full table - rotate the screen!
| Gas or Vapor | Formula | Specific Heat | Specific Heat Ratio | Individual Gas constant - R - | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cp (kJ/(kg K)) | cv (kJ/(kg K)) | cp (Btu/(lbmoF)) | cv (Btu/(lbmoF)) | κ = cp / cv | cp - cv (kJ/(kg K)) | cp - cv (ft lbf/(lbmoR)) | ||
| Acetone | (CH3)2CO | 1.47 | 1.32 | 0.35 | 0.32 | 1.11 | 0.15 | |
| Acetylene | C2H2 | 1.69 | 1.37 | 0.35 | 0.27 | 1.232 | 0.319 | 59.34 |
| Air | 1.01 | 0.718 | 0.24 | 0.17 | 1.40 | 0.287 | 53.34 | |
| Alcohol (ethanol) | C2H5OH | 1.88 | 1.67 | 0.45 | 0.4 | 1.13 | 0.22 | |
| Alcohol (methanol) | CH3OH | 1.93 | 1.53 | 0.46 | 0.37 | 1.26 | 0.39 | |
| Ammonia | NH3 | 2.19 | 1.66 | 0.52 | 0.4 | 1.31 | 0.53 | 96.5 |
| Argon | Ar | 0.520 | 0.312 | 0.12 | 0.07 | 1.667 | 0.208 | |
| Benzene | C6H6 | 1.09 | 0.99 | 0.26 | 0.24 | 1.12 | 0.1 | |
| Blast furnace gas | 1.03 | 0.73 | 0.25 | 0.17 | 1.41 | 0.3 | 55.05 | |
| Bromine | Br2 | 0.25 | 0.2 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 1.28 | 0.05 | |
| Butane | C4H10 | 1.67 | 1.53 | 0.395 | 0.356 | 1.094 | 0.143 | 26.5 |
| Carbon dioxide | CO2 | 0.844 | 0.655 | 0.21 | 0.16 | 1.289 | 0.189 | 38.86 |
| Carbon monoxide | CO | 1.02 | 0.72 | 0.24 | 0.17 | 1.40 | 0.297 | 55.14 |
| Carbon disulphide | CS2 | 0.67 | 0.55 | 0.16 | 0.13 | 1.21 | 0.12 | |
| Chlorine | Cl2 | 0.48 | 0.36 | 0.12 | 0.09 | 1.34 | 0.12 | |
| Chloroform | CHCl3 | 0.63 | 0.55 | 0.15 | 0.13 | 1.15 | 0.08 | |
| Coal gas | 2.14 | 1.59 | ||||||
| Combustion products | 1 | 0.24 | ||||||
| Ethane | C2H6 | 1.75 | 1.48 | 0.39 | 0.32 | 1.187 | 0.276 | 51.5 |
| Ether (diethyl ether) | (C2H5)2O | 2.01 | 1.95 | 0.48 | 0.47 | 1.03 | 0.06 | |
| Ethylene | C2H4 | 1.53 | 1.23 | 0.4 | 0.33 | 1.240 | 0.296 | 55.08 |
| Chlorodifluoromethane, R-22 | CHClF2 | 1.18 | ||||||
| Helium | He | 5.19 | 3.12 | 1.25 | 0.75 | 1.667 | 2.08 | 386.3 |
| Hexane | C6H14 | 1.06 | ||||||
| Hydrochloric acid | 0.795 | 0.567 | ||||||
| Hydrogen | H2 | 14.32 | 10.16 | 3.42 | 2.43 | 1.405 | 4.12 | 765.9 |
| Hydrogen Chloride | HCl | 0.8 | 0.57 | 0.191 | 0.135 | 1.41 | 0.23 | 42.4 |
| Hydrogen Sulfide | H2S | 0.243 | 0.187 | 1.32 | 45.2 | |||
| Hydroxyl | OH | 1.76 | 1.27 | 1.384 | 0.489 | |||
| Krypton | Kr | 0.25 | 0.151 | |||||
| Methane | CH4 | 2.22 | 1.70 | 0.59 | 0.45 | 1.304 | 0.518 | 96.4 |
| Methyl Chloride | CH3Cl | 0.240 | 0.200 | 1.20 | 30.6 | |||
| Natural Gas | 2.34 | 1.85 | 0.56 | 0.44 | 1.27 | 0.5 | 79.1 | |
| Neon | Ne | 1.03 | 0.618 | 1.667 | 0.412 | |||
| Nitric Oxide | NO | 0.995 | 0.718 | 0.23 | 0.17 | 1.386 | 0.277 | |
| Nitrogen | N2 | 1.04 | 0.743 | 0.25 | 0.18 | 1.400 | 0.297 | 54.99 |
| Nitrogen tetroxide | N2O4 | 4.69 | 4.6 | 1.12 | 1.1 | 1.02 | 0.09 | |
| Nitrous oxide | N2O | 0.88 | 0.69 | 0.21 | 0.17 | 1.27 | 0.18 | 35.1 |
| Oxygen | O2 | 0.919 | 0.659 | 0.22 | 0.16 | 1.395 | 0.260 | 48.24 |
| Pentane | C5H12 | 1.07 | ||||||
| Propane | C3H8 | 1.67 | 1.48 | 0.39 | 0.34 | 1.13 | 0.189 | 35.0 |
| Propene (propylene) | C3H6 | 1.5 | 1.31 | 0.36 | 0.31 | 1.15 | 0.18 | 36.8 |
| Water Vapor Steam 1 psia. 120 – 600 oF | H2O | 1.93 | 1.46 | 0.46 | 0.35 | 1.32 | 0.462 | |
| Steam 14.7 psia. 220 – 600 oF | H2O | 1.97 | 1.5 | 0.47 | 0.36 | 1.31 | 0.46 | |
| Steam 150 psia. 360 – 600 oF | H2O | 2.26 | 1.76 | 0.54 | 0.42 | 1.28 | 0.5 | |
| Sulfur dioxide (Sulphur dioxide) | SO2 | 0.64 | 0.51 | 0.15 | 0.12 | 1.29 | 0.13 | 24.1 |
| Xenon | Xe | 0.16 | 0.097 | |||||
Molar Mass Of Helium Gas
- κ = cp / cv - the specific heat capacity ratio
- cp = specific heat in a constant pressure process
- cv = specific heat in a constant volume process
For conversion of units, use the Specific heat online unit converter.

See also tabulated values of specific heat of food and foodstuff, metals and semimetals, common liquids and fluids, Common solids and other common substances as well as values of molar heat capacity of common organic substances and inorganic substances.
Related Topics
- Material Properties - Material properties for gases, fluids and solids - densities, specific heats, viscosities and more
- Thermodynamics - Effects of work, heat and energy on systems
Related Documents
- Air - Specific Heat at Constant Pressure and Varying Temperature - Online calculator, figures and tables showing how specific heat (Cp and Cv) of dry air vary with temperature at different pressures, SI and imperial units
- Air Specific Heat Ratio - Specific Heat Ratio of air at temperatures from -40 - 1000oC (-40 - 1500oF) at standard atmospheric pressure - Imperial and SI Units
- Argon - Thermophysical Properties - Chemical, Physical and Thermal Properties of Argon
- Compression and Expansion of Gases - Isothermal and isentropic gas compression and expansion processes
- Ethane - Density and Specific Weight - Online calculator, figures and tables showing density and specific weight of ethane, C2H6, at varying temperature and pressure - Imperial and SI Units
- Gases - Dynamic Viscosity - Absolute viscosities of gases
- Gases - Molar Specific Heat - Molar specific heats of gases at constant volume
- Heat Capacity - The heat capacity of a substance is the amount of heat required to change its temperature by one degree, and has units of energy per degree
- Heat, Work and Energy - Heat, work and energy tutorial - essentials as specific heat
- Ideal Gas Law - The relations between volume, pressure, temperature and quantity of a gas, including definition of density of a gas
- Molecular Weight of some Common Substances - Definition and molecular weight (molar mass) of some common substances
- Nitrogen - Specific Heat - Specific heat of Nitrogen Gas - N2 - at temperatures ranging 175 - 6000 K
- Nitrogen - Thermophysical Properties - Chemical, Physical and Thermal Properties of Nitrogen - N2
- Non-ideal gas - Van der Waal's Equation and Constants - Listing of van der Waals constants for more than 200 gases, used to correct for non-ideal behavior of gases caused by intermolecular forces and the volume occupied by the gas particles
- Ratios of Specific Heat of Gases - Ratios of specific heat for gases in constant pressure and volume processes
- Specific Heat - Online Unit Converter - Online specific heat converter with the most commonly used units
- Specific Heat of Solids - Common solids - like brick, cement, glass and many more - and their specific heats - in Imperial and SI units
- Specific Heat of some Liquids and Fluids - Specific heat for some common liquids and fluids - acetone, oil, paraffin, water and many more
- Sulfur Dioxide Liquid - Thermal Properties - Density, specific heat, thermal conductivity and more
- Total and partial pressure - Dalton's law of partial pressures - How to calculate total pressure and partial pressures for gas mixtures from Ideal Gas Law
Tag Search
Molar Mass Of Helium In G/mol
- en: specific heat capacity gases
- es: gases específicos de capacidad calorífica
- de: spezifische Wärmekapazität Gasen